BMC Gastroenterology :几种疾病与食物特异性IgG、IGg4抗体的相关性研究
发布日期:2018-12-18
原标题:食物特异性IgG4抗体不仅在小麦过敏的儿童中升高,胃肠疾病患儿中也会升高
延伸阅读
BMC Gastroenterology :
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-016-0450-3
Abstract :
Food sIgG and sIgG4 are highly individually versatile. We put a hypothesis that one of the responsible factors is the presence of gastrointestinal inflammatory diseases. The objectives were: 1. An analysis of wheat and rice sIgG and sIgG4 in healthy children, children with IgE-mediated wheat allergy (WA), coeliac disease (CD) and Helicobacter pylori infection (HP). 2. Usability of wheat sIgG and sIgG4 in the WA diagnostics.
Methods
We compared 388 each wheat and rice sIgG and sIgG4 in a group of 200 children: 50 WA (diagnosis, diet treatment, tolerance), 50 CD (diagnosis and remission), 50 HP and 50 healthy. SIgE, sIgG, sIgG4 were determined with the FEIA method (Pharmacia CAP System).
Results
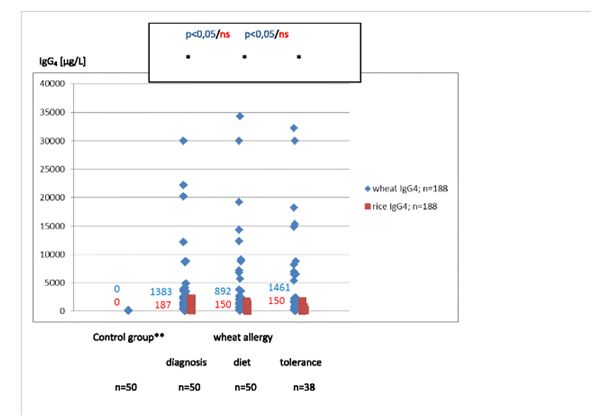
In healthy children food sIgG were the lowest; no sIgG4 were found. In the CD diagnosis group wheat and rice sIgG and rice sIgG4 were the most common and their concentrations were the highest. Wheat sIgG4 were the highest in WA children (diagnosis and tolerance) to fall during the elimination diet (p < .05). Wheat and rice sIgG remained the same in all allergy phases. Rice sIgG also did not differ in the class G4.
Conclusions
1.Serum concentrations of wheat and rice sIgG and sIgG4 are elevated in children with CD, HP and WA. 2. Sub-clinical incidence of some gastrointestinal inflammatory diseases may be responsible for high individual versatility of food sIgG and sIgG4 concentrations in serum. 3. Wheat sIgG and sIgG4 in children do not correlate with WA clinical picture.
All Authors:Grażyna Czaja-Bulsa Email author, Michał Bulsa and Aneta Gębala


——来自浙大迪迅
①背景食物sIgG和sIg G4具有高度的个体多样性。我们假设,胃肠道炎症的存在是导致其产生的原因之一。本研究的目的是:1、对以下几组儿童样本进行小麦和大米sIgG和sIgG4分析:健康儿童、IgE介导的小麦过敏(WA)、乳糜泻(CD)和幽门螺杆菌感染(HP)。2。评价小麦sIgG和sIgG4检测在小麦过敏诊断中的适用性。②我们比较了200名儿童的小麦和大米sIgG和sIgG4(总计388项): 50 例小麦过敏(诊断、饮食治疗、耐受)、50乳糜泻(诊断和缓解)、50 幽门螺杆菌感染(HP)和50 例健康人。采用FEIA法(Pharmacia CAP系统)测定SIgE、sIgG、sIgG4。③结果:健康儿童食品中sIgG最低,没有发现sIgG4。乳糜泻组以小麦和大米sIgG、大米sIgG4最为常见,其浓度最高。小麦sIgG4在小麦过敏儿童中过敏儿童(诊断和耐受)中最高,在饮食排除期间下降 (p < .05)。小麦和大米sIgG在所有过敏阶段保持不变。大米sIgG和大米sIgG4没有什么差异。④结论1.CD、HP和WA患儿血清中小麦和水稻sIgG和sIgG4浓度升高。2。某些胃肠道炎症的亚临床发生率可能是导致血清中食物sIgG和sIgG4浓度的高度个体多样性的原因。3.儿童小麦sIgG和sIgG4的浓度与小麦过敏临床表现不成对应关系。
延伸阅读
BMC Gastroenterology :
[IF:2.818]
Food IgG4 antibodies are elevated not only in children with wheat allergy but also in children with gastrointestinal diseaseshttps://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-016-0450-3
Abstract :
Food sIgG and sIgG4 are highly individually versatile. We put a hypothesis that one of the responsible factors is the presence of gastrointestinal inflammatory diseases. The objectives were: 1. An analysis of wheat and rice sIgG and sIgG4 in healthy children, children with IgE-mediated wheat allergy (WA), coeliac disease (CD) and Helicobacter pylori infection (HP). 2. Usability of wheat sIgG and sIgG4 in the WA diagnostics.
Methods
We compared 388 each wheat and rice sIgG and sIgG4 in a group of 200 children: 50 WA (diagnosis, diet treatment, tolerance), 50 CD (diagnosis and remission), 50 HP and 50 healthy. SIgE, sIgG, sIgG4 were determined with the FEIA method (Pharmacia CAP System).
Results
In healthy children food sIgG were the lowest; no sIgG4 were found. In the CD diagnosis group wheat and rice sIgG and rice sIgG4 were the most common and their concentrations were the highest. Wheat sIgG4 were the highest in WA children (diagnosis and tolerance) to fall during the elimination diet (p < .05). Wheat and rice sIgG remained the same in all allergy phases. Rice sIgG also did not differ in the class G4.
Conclusions
1.Serum concentrations of wheat and rice sIgG and sIgG4 are elevated in children with CD, HP and WA. 2. Sub-clinical incidence of some gastrointestinal inflammatory diseases may be responsible for high individual versatility of food sIgG and sIgG4 concentrations in serum. 3. Wheat sIgG and sIgG4 in children do not correlate with WA clinical picture.
All Authors:Grażyna Czaja-Bulsa Email author, Michał Bulsa and Aneta Gębala
2018-11-30 Article
创建过敏性疾病的科研、科普知识交流平台,为过敏患者提供专业诊断、治疗、预防的共享平台。

开云电子(中国)官方网站 | 华亿首页(中国)网页版 | 开云网页版 | 天博手机网页(中国)有限公司 | 千亿体育线上平台中国有限公司 | 米兰手机在线登入 | 米乐官方网页版 | 华亿网页版 | 三亿体育首页(中国)网站首页 |
 华亿体育(中国)游戏平台
华亿体育(中国)游戏平台

